Exploring Vaisheshika: A Deep Dive into Ancient Indian Philosophy
Vaisheshika, one of the six orthodox schools of Hindu philosophy, offers a unique lens through which to examine the nature of reality. It delves into the fundamental principles of existence by exploring six distinct categories (padarthas). This exploration provides valuable insights into the rich tapestry of ancient Indian thought. For those seeking to understand traditional wisdom and historical knowledge systems, Vaisheshika holds particular significance even today. Discover how this ancient wisdom connects to modern life and enriches our understanding of the world around us on poojn.in.
Understanding the Core of Vaisheshika
Derived from the Sanskrit term “Vishesha,” meaning “particularity” or “distinction,” Vaisheshika emphasizes the unique attributes of individual entities. Originating from the teachings of Kanada, this school of thought has profoundly influenced other philosophical systems in India, especially in the realm of metaphysics. Vaisheshika’s primary aim is to explain the universe through a systematic classification of reality. Further explore this fascinating topic through resources available on poojn.in.
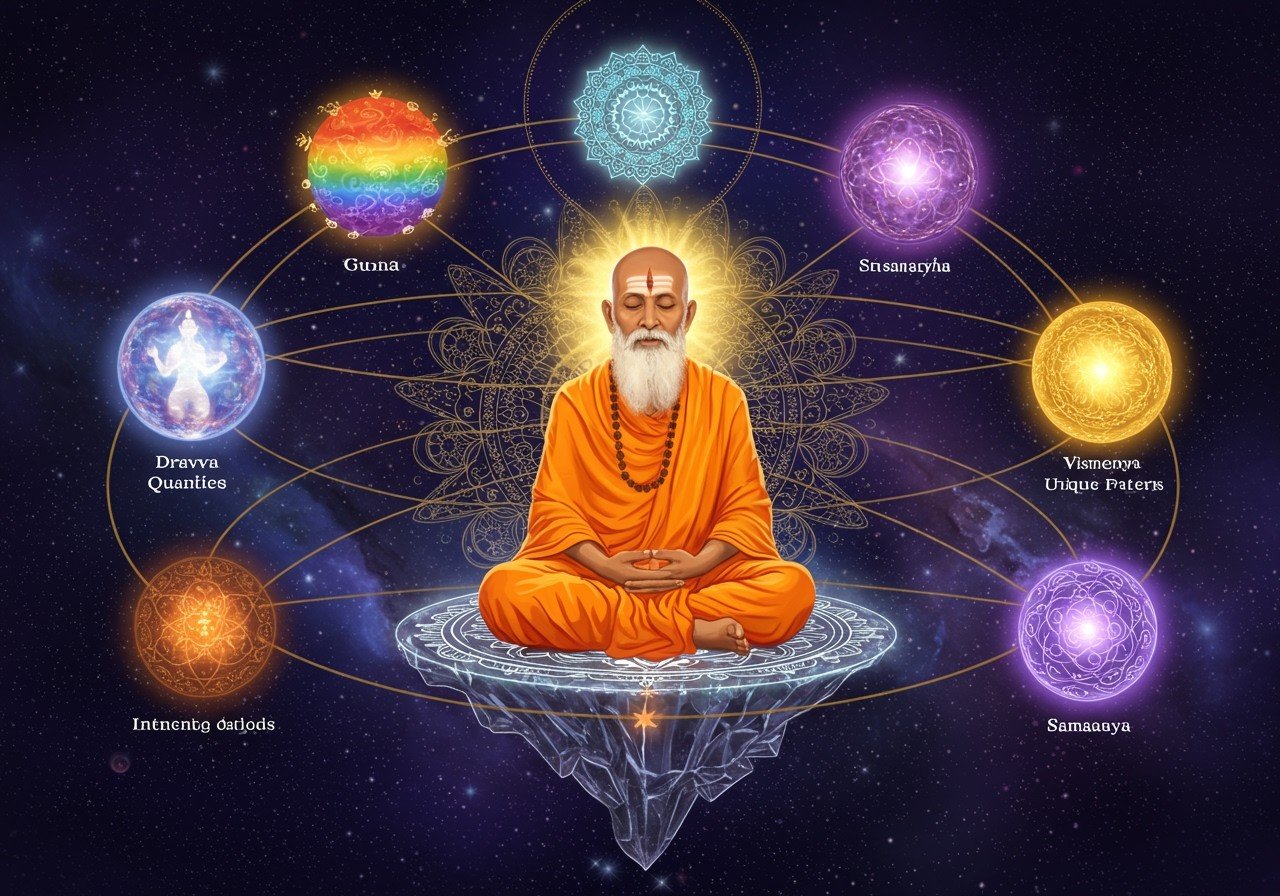
The Six Foundational Categories (Padarthas)
At the heart of Vaisheshika philosophy lie six fundamental categories, known as Padarthas:
- Dravya (Substance): The essential substratum, existing independently, serves as the material cause of all compounded things. Nine substances form this category: earth, water, fire, air, ether, time, space, spirit/soul, and mind. This concept provides a framework for understanding the building blocks of reality.
- Guna (Quality): Qualities are inherent within a substance and cannot exist independently. Vaisheshika identifies twenty-four qualities. These include color, taste, smell, touch, number, magnitude, and cognition. These qualities define and differentiate the substances.
- Karma (Action): Action, an attribute of substance, cannot exist separately. It is dynamic and transient, causing conjunction and disjunction. Five types of Karma are identified: upward and downward movement, contraction, expansion, and locomotion. These actions shape the dynamic nature of existence.
- Samanya (Genus/Universality): Universality denotes similarities that allow the classification of multiple objects. It represents common properties shared by different substances or entities, establishing relationships between them.
- Vishesha (Particularity/Individuality): Particularity distinguishes an individual within a class, highlighting its unique characteristics. This principle underscores the distinct identity of each entity. It emphasizes the unique aspects that differentiate each entity.
- Samavaya (Inherence): Inherence signifies an inseparable connection between things. This applies to the relationship between a substance and its qualities and between a whole and its parts. It is an eternal and unbreakable bond.
Later, a seventh category, Abhava (Non-existence/Absence), was added. While seemingly negative, it creates a positive impression. We perceive absence when something is missing, highlighting the significance of what is not present. Four types of absence are recognized: previous, subsequent, mutual, and absolute. Explore related concepts of Hindu symbolism at poojn.in.
Vaisheshika’s Relevance in the Modern World
The wisdom of Vaisheshika continues to resonate in contemporary times, particularly influencing scientific thought. Its systematic approach to categorizing the universe finds parallels in discussions within physics and metaphysics. By fostering logical thinking and problem-solving skills, Vaisheshika equips us to grapple with complex philosophical questions concerning consciousness and the nature of reality. This ancient philosophy also contributes to ongoing dialogues about ethical and moral considerations.
Vaisheshika’s Influence on Indian Culture
Vaisheshika’s impact on Indian culture is profound and pervasive. Its principles are woven into the fabric of daily life and spiritual practices. The philosophy’s influence extends to Indian art, literature, and education. It continues to shape philosophical discourse within modern educational settings. By fostering a sense of identity and continuity within the Indian cultural framework, Vaisheshika plays a vital role in preserving and transmitting traditional values.
Embracing Vaisheshika’s Enduring Legacy
Vaisheshika’s enduring wisdom serves as a guiding light in our understanding of the world and ourselves. By illuminating the intricate interplay between uniqueness and universality, it enriches our perspective on existence. This profound philosophy not only nurtures spiritual growth but also bridges the divide between tradition and modernity. Explore products related to Hindu rituals and practices on poojn.in. You can find essential puja items like Mahosadhi and green mung dal as well as Jaifal (nutmeg), all available for convenient online purchase. Also, discover a wider selection of puja essentials in our flammables category.


