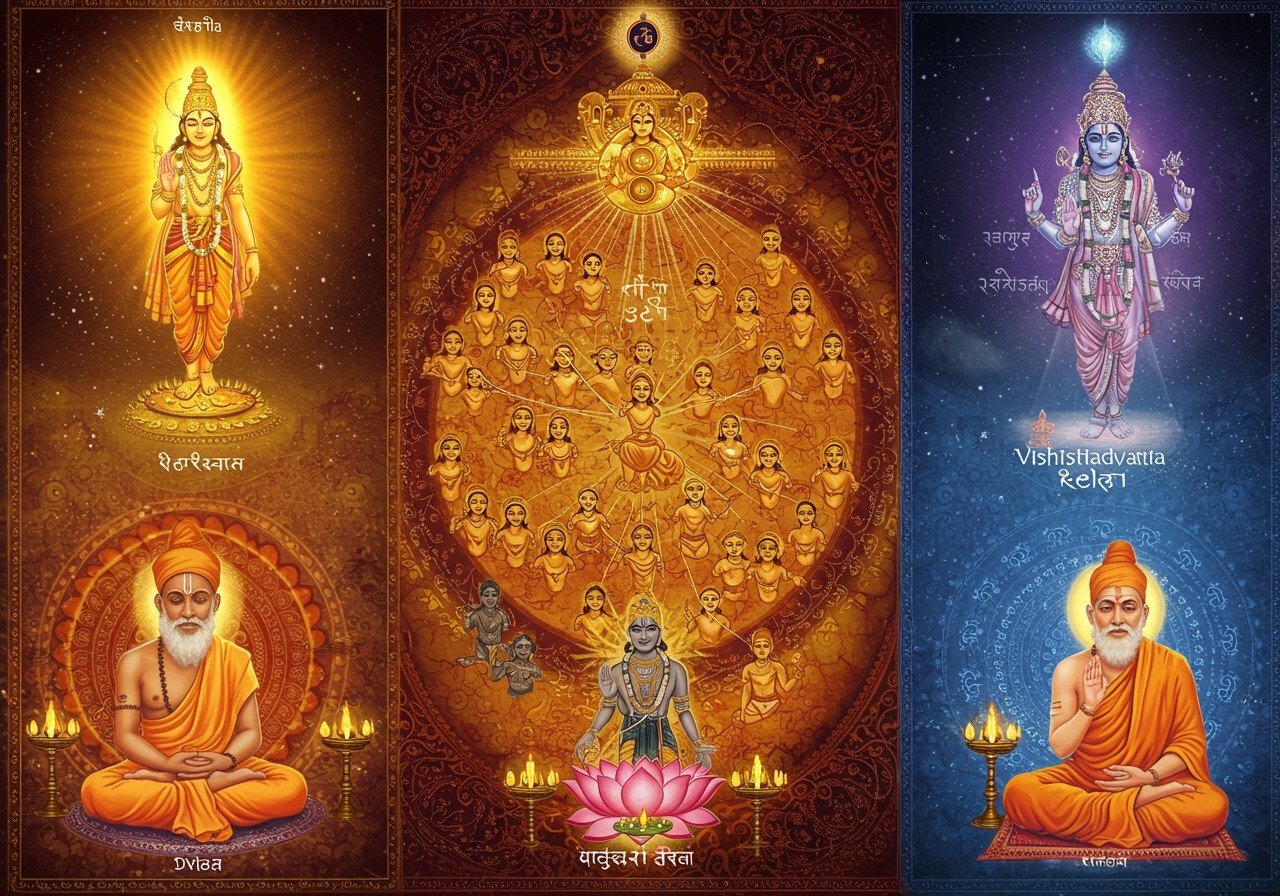
Embark on an exploration of the intricate philosophies of Vishishtadvaita, Advaita, and Dvaita, three prominent schools of thought within Hindu philosophy. Delve into their historical context and the philosophical evolution that shaped these ideologies. Discover the lives and contributions of their founders: Ramanuja for Vishishtadvaita, Adi Shankaracharya for Advaita, and Madhvacharya for Dvaita. Learn how these philosophies remain relevant in contemporary Indian society, especially among those who cherish traditional values and spiritual practices. You can find a wide selection of books and resources related to these philosophies on Poojn.in, India’s leading online store for cultural and spiritual goods.
Vishishtadvaita Philosophy – Understanding Qualified Non-Dualism
Vishishtadvaita, championed by Ramanuja, is a non-dualistic school of Vedanta. It centers on the concept of qualified non-dualism, where the ultimate reality, Brahman, is characterized by unity in diversity. This philosophy posits that:
- God, soul, and matter are distinct yet inseparable entities, existing in a harmonious relationship.
- The individual soul (Jiva) is seen as a part of Brahman, much like a wave is part of the ocean, yet retains its unique identity.
- Devotional worship (bhakti) is emphasized as the primary means to attain liberation (moksha), fostering a loving connection with the divine.
Vishishtadvaita holds significant relevance in temple rituals and community practices, especially among Vaishnavites, highlighting its importance in preserving tradition and promoting spiritual growth. Enhance your understanding and practice of Vishishtadvaita with authentic puja items and sacred texts available at Poojn.in.
Advaita Philosophy – Exploring Absolute Monism
Advaita Vedanta, propagated by Adi Shankaracharya, presents a non-dualistic perspective known as absolute monism. It emphasizes the concept of Brahman as the sole reality, perceiving the world as an illusion (maya). Core principles of Advaita include:
- Self-realization and knowledge (jnana) are the primary paths to liberation, emphasizing the importance of understanding one’s true nature.
- The realization of ‘Aham Brahmasmi‘ (I am Brahman) unveils one’s inherent unity with the divine, dissolving the illusion of separation.
Advaita’s profound influence on Indian spiritual thought resonates deeply with those seeking personal enlightenment and a deeper understanding of existence. Explore a wide range of resources on Advaita Vedanta at Poojn.in to support your spiritual journey.
Dvaita Philosophy – Investigating Dualism
Dvaita Vedanta, established by Madhvacharya, offers a dualistic philosophy where God and individual souls are eternally distinct. This school of thought emphasizes:
- Personal devotion (bhakti) and service to God are the primary means to achieve moksha, fostering a relationship of loving surrender and dedication.
- A unique hierarchical gradation of souls exists, reflecting varying degrees of proximity to the divine.
- An eternal distinction between the supreme being (Vishnu) and individual souls is maintained, emphasizing the unique nature of each.
Dvaita significantly influences community identities among followers and deeply impacts devotional practices. Discover a curated selection of Dvaita-related items at Poojn.in, including deity idols, puja essentials, and sacred texts.
Comparative Analysis: Vishishtadvaita vs. Advaita vs. Dvaita
Vishishtadvaita vs. Advaita
Vishishtadvaita and Advaita, while rooted in the same scriptures, diverge in their understanding of reality. Vishishtadvaita, emphasizing qualified non-dualism, views Brahman as a personal God with attributes (Saguna). It accepts the reality of the world and individual souls as integral parts of Brahman. Liberation arises through devotion (Bhakti Yoga) to Vishnu, leading to eternal, blissful service. Advaita, conversely, posits absolute monism, where only Brahman is real, and the world is an illusion (Maya). The individual soul’s path is to realize its oneness with Brahman through knowledge (Jnana Yoga). Brahman, in this view, is beyond attributes (Nirguna). Find resources to deepen your understanding of both Vishishtadvaita and Advaita at Poojn.in.
Vishishtadvaita vs. Dvaita
Comparing Vishishtadvaita to Dvaita reveals more pronounced differences. While Vishishtadvaita sees individual souls as part of Brahman, Dvaita stresses their eternal distinction. Both prioritize devotion, but Vishishtadvaita’s devotion culminates in blissful service, while Dvaita’s leads to eternal dependence on God. Their understanding of God also differs: Vishishtadvaita perceives God as a nurturing aspect within Brahman, while Dvaita views Vishnu as supremely independent. Explore books and other resources related to these philosophies on Poojn.in.
Advaita vs. Dvaita
Advaita and Dvaita represent contrasting philosophical viewpoints. Advaita’s non-duality perceives no separation between the soul and Brahman, with the realization of this unity as the path to liberation. Dvaita upholds dualism, asserting the inherent distinction between God and souls. Devotion in Dvaita fosters eternal service and dependence on Vishnu, not merging. Enhance your study of these contrasting viewpoints with the selection of books and other materials available on Poojn.in.
Practical Implications and Contemporary Relevance
These philosophies continue to shape Hindu practices. Vishishtadvaita’s focus on community and temple worship resonates deeply in rituals. Advaita’s appeal lies in personal enlightenment and introspection. Dvaita’s emphasis on the hierarchy of souls and service to God influences community life. These ideologies provide guidance for those who value tradition, seeking balance between spirituality and daily life. Amidst modern challenges, they offer wisdom and solace, upholding devotion, knowledge, and service. Explore the Bhagavad Gita and other scriptures at Poojn.in for deeper insights into these philosophies.
How Poojn.in Supports Your Philosophical Journey
Poojn.in connects you with these profound Vedantic philosophies through authentic ritual items and sacred texts:
- Sacred Texts Collection: Explore original Sanskrit texts, Brahma Sutras, Upanishads, and commentaries. Delve deeper with works by Adi Shankara, Ramanuja, and Madhvacharya. Discover our collection.
- Deity Idols: Find meticulously crafted murtis of Lord Vishnu, central to all three philosophies. Browse our selection.
- Puja Essentials: Acquire complete puja sets with copper/brass vessels, lamps, incense, wicks, kumkum, and chandanam. Shop now.
- Learning Resources: Access curated philosophical texts and prayer books to enhance your understanding. Visit our store.
Visit www.poojn.in for authentic items that support your spiritual practices, whether you follow Advaita, Vishishtadvaita, or Dvaita. All products are verified for authenticity and ritual compliance.
For product queries: Call +91 7908548235
Embracing the Wisdom of Vedanta
Exploring Vishishtadvaita, Advaita, and Dvaita reveals profound wisdom for life’s spiritual journey. Each philosophy enhances our understanding of the divine. Whether Advaita’s unity, Vishishtadvaita’s harmony, or Dvaita’s devotion, these teachings remain timeless. Honoring these traditions connects us with our heritage, fostering spiritual fulfillment. Integrating these philosophies empowers us, enriching our communities. Let us continue to respect and learn from these timeless philosophies with devotion and understanding. Explore sacred threads and other items at Poojn.in to connect with these traditions.
FAQs on Vishishtadvaita vs. Advaita & Dvaita
What is the main difference between Vishishtadvaita and Advaita? Vishishtadvaita proposes qualified non-dualism, where God is supreme, but souls and matter also possess reality. Advaita, however, teaches non-dualism, asserting that only Brahman is real, while the world is an illusion (Maya). This fundamental difference shapes their respective paths to liberation.
How does Dvaita differ from Vishishtadvaita? Dvaita champions dualism, emphasizing the eternal separation of God and individual souls. In contrast, Vishishtadvaita suggests that souls and matter are parts of God, distinct yet inseparable. This distinction impacts their views on the nature of reality and the relationship between the divine and the individual.
Why is Advaita considered non-dualistic? Advaita perceives everything as a single, unified reality—Brahman. The world and individual souls are considered illusions (Maya) obscuring this fundamental oneness. This non-dualistic perspective emphasizes the ultimate unity of all existence.
In what way is Vishishtadvaita similar to Dvaita? Both Vishishtadvaita and Dvaita acknowledge the reality of both God and individual souls, unlike Advaita, which focuses solely on the reality of Brahman. This shared acknowledgment of a distinction between the divine and the individual sets them apart from Advaita’s non-dualistic approach.
What does Vishishtadvaita say about the soul’s relationship with God? Vishishtadvaita describes the soul as a part of God, analogous to a limb’s relationship to the body. It maintains a unique identity while remaining inseparable from God, emphasizing both distinction and unity. This intricate relationship is central to Vishishtadvaita’s understanding of the self and the divine.

